National arms of Iceland: Difference between revisions
Knorrepoes (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Knorrepoes (talk | contribs) m (Text replacement - "|Arms of {{PAGENAME}}]]" to "|Coat of arms (crest) of {{PAGENAME}}]]") |
||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
{|align="center" | {|align="center" | ||
|align="center"|[[File:island7.jpg|center| | |align="center"|[[File:island7.jpg|center|Coat of arms (crest) of {{PAGENAME}}]] <br/>Seals of Bergen merchants from 1414 (left) and 1515 (right) | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 14:41, 20 August 2023
THE NATIONAL ARMS OF ICELAND
Official blazon
Skjaldarmerki Íslands er silfurlitur kross í heiðbláum feldi, með eldrauðum krossi innan í silfurlita krossinum. Armar krossanna skulu ná alveg út í rendur skjaldarins á alla fjóra vegu. Breidd krossmarksins skal vera 2/9 af breidd skjaldarins, en rauði krossinn helmingi mjórri, 1/9 af breidd skjaldarins. Efri reitirnir skulu vera rétthyrndir, jafnhliða ferhyrningar og neðri reitirnir jafnbreiðir efri reitunum, en þriðjungi lengri. Skjaldberar eru hinar fjórar landvættir, sem getur í Heimskringlu: Griðungur, hægra megin skjaldarins, bergrisi, vinstra megin, gammur, hægra megin, ofan við griðunginn, og dreki, vinstra megin, ofan við bergrisann. Skjöldurinn hvílir á stuðlabergshellu.
Origin/meaning
The arms were adopted in 1944 at the independence of Iceland from Denmark.The arms of Iceland are based on the flag of the country. The arms stand on basalt, the main rock of which Iceland is made. The supporters refer to the 12th century saga of Heimskringla. In this saga the King of Denmark, Harald Blueteeth Gormsson, wants to conquer Iceland and sends out a Finnish magician to see whether it was possible to conquer the country. He first lands in the East coast in the present day Vopnafjörður. There he encounters a fierce dragon, that forces him to sail away. In his second attempt, in the north of the country, a giant eagle awaits him and he decides not to go ashore there. In the western part of the country a huge bull forces him back to see again and finally in the south a giant savage makes him decide that the country can not be conquered. The four figures are since then named the Protectors of the country.
The probable origin of the supporters, however, is less poetic; they are derived from the symbols of the four Evangelists, Luke (bull), Marc (lion, became dragon), John (eagle) and Matthew (man became giant), which have been adopted/changed to symbols from the more common Norse mythology by the author of Heimskringla.
From 1919-1944 the arms were practically similar, except that the protectors were gold, a crown was placed on the shield and the arms were not placed on basalt. Iceland was at the time an independent State in personal union with Denmark.
| The arms of Iceland from 1919-1944 |
The oldest known arms of Iceland show the lion of Norway placed on a divided shield. The arms are known from the 13th century, when Iceland was a possession of the Norwegian kings.
| The arms of Iceland from the 13th century |
During the middle ages, and until 1903 the arms of Iceland were a crowned dried cod. Dried cod was the main source of income in the middle ages and the symbol was thus a symbol of wealth. The oldest use of the cod is known from Hanseatic merchants from Bergen (Norway), who had the exclusive trade with Iceland. To symbolise this exclusive right they added the dried cod to their arms. In the oldest seals, dating from 1414 the cod is not yet crowned. In a seal from 1515 the cod has a crown.
| Seals of Bergen merchants from 1414 (left) and 1515 (right) |
The cod is also seen on a codex, the Stockholm-codex, from 1360. It is placed in the margin of the text, but it is not quite sure whether it actually refers to an Icelandic symbol.
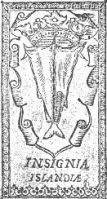
The first time that the cod is placed on a shield and is used as the national symbol, is in a book of psalms issued in Hólar in 1589. The text states also Insigniae Islandiae.
In 1874 the independence movement was searching for a new symbol. It was finally decided that the falcon would be the new national symbol and subsequently new arms showing the falcon were granted on December 11, 1903 and used from 1903-1918. The Icelandic gyrfalcon has through the years been a very popular bird of prey. It is also a typical Icelandic bird. The falcon has also been used by old Icelandic chieftains on their seals in the 15th century. The arms were replaced by the new arms in 1919.
The arms in the Wapen- en Vlaggenboek van Gerrit Hesman (1708)
The arms in the Abadie albums
The arms on a Dutch Willem II cigar band
Literature : Halldó Hermannsson, Skjaldmerki Íslands, Eimreiðin 22(1916)157-178.
Iceland heraldry portal
This page is part of the Iceland heraldry portal |
Heraldry of the World |
|
Civic heraldry:
|
Other heraldry: |
Contact and Support
Partners:
Your logo here ?
Contact us
© since 1995, Heraldry of the World, Ralf Hartemink 
Index of the site